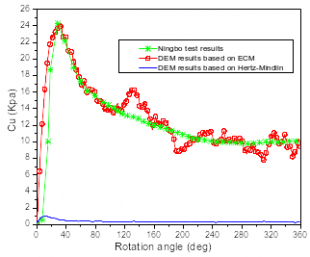
The soft soil possess the characteristic of high water content, high sensitivity and low shear stress. It may cause the problems like tunnel surrounded with the soft soil undergoes the excavation by tunnel boring machine (TBM) , the long-term additional settlement of the soft soil arise from the disturbance by excavation has an adverse effect on the infrastructure. Measurement of in-situ soil properties of this area is therefore important. We have conducted field experiments on subsoil which consist of soft soil in southeast of China before and after operation of trains, we also conducted laboratory test like triaxial test on soft soil dug up from testing site to explore the mechanical properties. One of them is shear vane test which is used for measuring the undrained shear stress of soft soil, as an in-suit test method, the disturbance of soil during the test can be neglected, so shear vane test is regarded as the method to reflect the in-suit shear stress. However the understanding of shear vane test of the internal shearing mechanisms is not well understand and the use of numerical modelling to provide further scientific insights for the soft soil under shearing need to be carried out. But soft soil which comprising clumps consist of soil particles in essence has discrete nature. In consideration of its discrete nature, discrete element method has an advantage of simulating soft soil. Firstly, an elasto-plastic adhesive contact model has been proposed, this model takes cohesive force between particles, plastic deformation after loading and unloading into considerate. Secondly, we simulated shear vane test based on this contact model as fig 1 shows, the variation of torque during shearing process is highly similar with the field test, the comparison between DEM and experimental results are put in fig 2. We also found the contact model can capture the behavior of model under different stress history which is an important features of soft soil. Then, we analysis the effect of parameters on the simulation, included the constant value which simulate the Van Der Waals force, the ratio of plastic deformation, loading/unloading stiffness and particle tangential friction coefficient. Thirdly, we calculate the bulk stress of the numerical of shear vane test to analysis the shear stress distribution along the vane blade during the simulation. The shear stress distribution along the vane is important when we calculate the shear strength from torque of vane. We also monitor the development of shearing process between micro and macro scape to explore the inner mechanisms of shear vane test.
This work we proposed a contact model in discrete element method which can reproduce the behavior of soft soil in shear vane test, and we can see the potential to simulate more complex behavior based this model of soft soil or other cohesive materials in the future. Then we compare the macro and micro results in pre-peak, peak, post peak states in shear vane test, we linked the particle behavior with bulk behavior to explore the inner mechanisms. The shear stress distribution along the vane and the difference with the conventional assumption was studied at last.

![The shear vane test model built with the DEM software EDEM. [Note: the grey colour represents the vane and consists of two perpendicular blades and the rigid solid particles were generated in fixed boundary]; The shear vane test model built with the DEM software EDEM. [Note: the grey colour represents the vane and consists of two perpendicular blades and the rigid solid particles were generated in fixed boundary];](https://eng.ed.ac.uk/sites/eng.ed.ac.uk/files/styles/medium-2/public/images/research/projects/1.png?itok=JyJoyZkx)