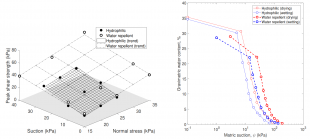
Water repellent (WR) granular soils (Figure 1) present an innovative solution to this problem [1, 2, 3]. Hydrophobisation can arise naturally (e.g., due to deposition of organic matter, treatment with wastewater or wildfire), but can also be achieved in laboratory conditions by chemical treatment, typically with dimethyldichlorosilane (DMDCS). Besides being resilient to volumetric change under changes in saturation, water repellent soils have been shown to slow down water and root penetration, thus making them a potential candidate for waste storage liners. However, the effect of water repellency on soil strength and permeability is not well understood (Figure 2). This new PhD project will examine the fundamental behaviour of WR soils and how they can be used in the field.
References
[1]L.F DeBano. Water repellency in soils: a historical overview. Journal of Hydrology, 231-232:4 – 32, 2000.
[2]S. D. N. Lourenço, Y. Saulick, S. Zheng, H. Kang, D. Liu, H. Lin, and T. Yao. Soil wettability in ground engineering: fundamentals, methods, and applications. Acta Geotechnica, 13(1):1– 14, 2018.
[3]C. T. S. Beckett, A. B. Fourie, and D. G. Toll. Water repellent soils: The case for unsaturated soil mechanics. In the 3rd European Conference on Unsaturated Soils. E-UNSAT 2016, 2016.